About DBWS Program
As is now well known, the Rietveld method is a powerful tool for
the extraction of structural information from powder diffraction
patterns, quantitative phase analysis, and obtaining microstructural
information. It is valuable to people working on a diverse range of
problems. In the last 15 years, the Rietveld Method has played a
crucial role in almost every high profile area of new materials
research. It was extensively used for the study of high temperature
("HiTc") superconductors, it has played a key role in developing
the solid state chemistry of the fullerenes, and it is currently
being used to study colossal magnetoresistance materials,
thermoelectrics and negative thermal expansion ceramics.
Additionally, it has also been used for thousands of structural
studies of metal oxide catalysts, zeolites, clays, minerals, battery
materials, pharmaceuticals, biological materials, and even polymers,
using both X-ray and neutron powder diffraction data. Quantitative
phase analysis utilizing Rietveld Refinement (RR) is now an especially
important ancillary procedure, as it can offer superior results to
the more traditional methods. RR is of use for environmental problems,
and analyses for the minerals processing and the petrochemicals industries.
The determination of crystallite size and microstrain parameters via use
of the Rietveld method is also a growing field.
Rietveld refinement is not a structure solution method; it is a crystal
structure refinement method. Because the refinement process is a non-linear
least squares process, the refinement must be started from a "reasonably good"
model of the crystal structure and the experiment. That model has to be
supplied by the user. Rietveld refinement is not a "black box" or "turn key"
operation. It requires substantial, knowledgeable operator interaction.
DBWS is a DOS program but it can be operated quite effectively in a Windows
environment, e.g., Windows 95 or 98. (See p. 8 of the Userís Guide) If Windows
NT is to be used,it is necessary to assure that the "run" command is preserved
when the various "policy" options are selected.
DBWS accepts powder X-ray diffraction data in a number of formats(see pages
11 and 37-40.) and neutron diffraction (nuclear scattering only)in one common
format. However, all data must be digitized and provide the intensities at
equal steps in scattering angle (2 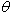 ) )
A number of changes have recently been made in DBWS to facilitate and enhance
its use for quantitative phase analysis(QPA). It is now possible to use it for
QPA both with and without an internal standard and in the presence of an
amorphous component (see pp. 19-21)
The DBWS program also offers convenient calculation of the powder diffraction
patterns corresponding to the crystal structural and instrumental parameters
provided by the user.
|